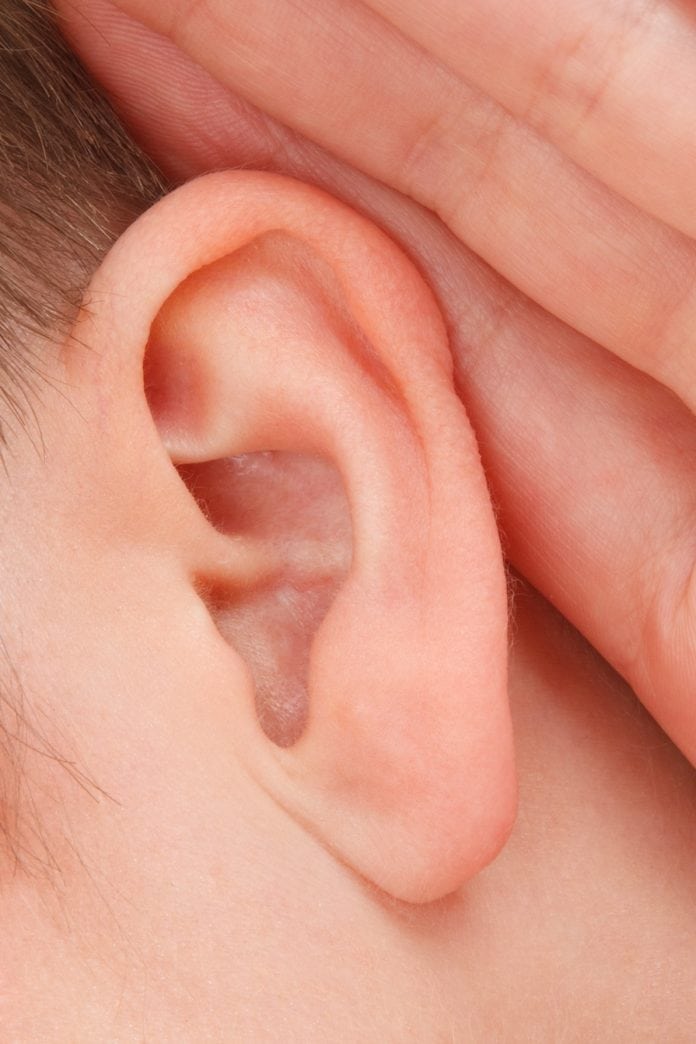
Researchers have identified new inner ear neurons, which may lead to new hearing therapies to treat disorders.
The team at the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified four types of neurons in the inner ear, three of these are completely new to science, which may develop new hearing therapies.
How has this developed scientific knowledge of the inner ear?
Sound reaches the inner ear after being converted into electrical signals and being relayed to the brain by the cochlea. The cochlea uses nerve cells to relay the information to the brain. Previously, scientists thought that most of these cells were either type one or type two neurons, with type one neurons transmitting most of the sounds. The new study has changed that knowledge by showing that type one cells include three different types of cell. This comes after previous research variations which indicated variations in the electrical properties and sonic response of type one cells. The new study explains the reason for this variation, and may help to develop new hearing therapies as a result.
Francois Lallemend, the research group leader at the Department of Neuroscience at the Karolinska Institutet who led the study, said: “We now know that there are three different routes into the central auditory system, instead of just one…this makes us better placed to understand the part played by the different neurons in hearing. We’ve also mapped out which genes are active in the individual cell types.”
How will this help to develop new hearing therapies?
Lallemend added: “Our study can open the way for the development of genetic tools that can be used for new treatments for different kinds of hearing disorders, such as tinnitus…Our mapping can also give rise to different ways of influencing the function of individual nerve cells in the body.”
Some hearing disorders, such as tinnitus and hyperacusis, are affected by the decoding of sonic intensity. Decoding sonic intensity is an essential function which allows a person to filter out background noise and hear conversations when the external environment is loud. The study has been able to show that the three neuron types play a part in this function.






















How quickly is this research ready to use and How will this help my 99 year old Mother who they diagnose with profound hearing loss. The hesring aids recommended hurt her ears.