B Medical Systems discusses how the company’s Blood Management Solutions can expertly preserve blood to help those affected by bleeding disorders.
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions that result from improper blood clotting. During normal clotting, platelets create a plug at the site of an injured blood vessel.
They combine with proteins known as clotting factors to form a fibrin clot, essentially a gel plug that holds the platelets in position and enables the injury site to heal while preventing blood from escaping the blood vessel.
Although excessive clotting can lead to conditions such as heart attacks and strokes, the inability to form clots can result in excessive bleeding, which is also extremely hazardous.
The causes of bleeding disorders
Excessive bleeding can be caused by abnormal blood vessels or abnormal or insufficient platelets and clotting proteins. Bleeding disorders that cause such issues can be inherited (such as Haemophilia, Von Willebrand disease, etc.) or acquired during the lifetime (such as liver disease-associated bleeding, Vitamin K deficiency bleeding, etc.).
Haemophilia is one of the most common genetically inherited bleeding disorders affecting more than 234 thousand people worldwide. This genetic disease does not allow the blood to clot properly due to the lack of or very low levels of clotting factors.
Internal bleeding can be caused in the joints and lead to chronic joint pains or even happen in the brain, causing serious problems such as seizures and paralysis.
Based on the types of clotting factors, the two most common types of Haemophilia are Haemophilia A, a classic form caused by the lack or decrease of clotting factor VIII, and Haemophilia B, which is caused by the lack or decrease of clotting factor IX.
Haemophilia affects more males than females because it is an X chromosome-linked disease, and the genes for factor VIII and factor IX are located on that chromosome. Haemophilia A affects 1 in 5000 male births and can be diagnosed at a very young age.
Genetic tests can be done during pregnancy to know if the baby will have the disorder and can even detect the chances of it being passed on from a pregnant mother to the baby.

Treatment options for bleeding disorders
Haemophilia cannot be cured, but it is possible for the people affected to have a normal life with lifelong prophylactic treatment, for which they need to be trained and prepared.
The best way to treat bleeding disorders is to replace the missing clotting factor, known as factor replacement therapy, which is done by injecting concentrates of the clotting proteins intravenously.
The two main types of clotting factor concentrate available are plasma-derived factor concentrates and recombinant factor concentrates. In the first case, the clotting factors are mainly obtained by processing blood plasma to obtain the necessary proteins.
While in the case of the concentrates, animal cells are engineered to produce the clotting factors. Either way, both solutions need to be stored and handled safely to ensure their potency until use.
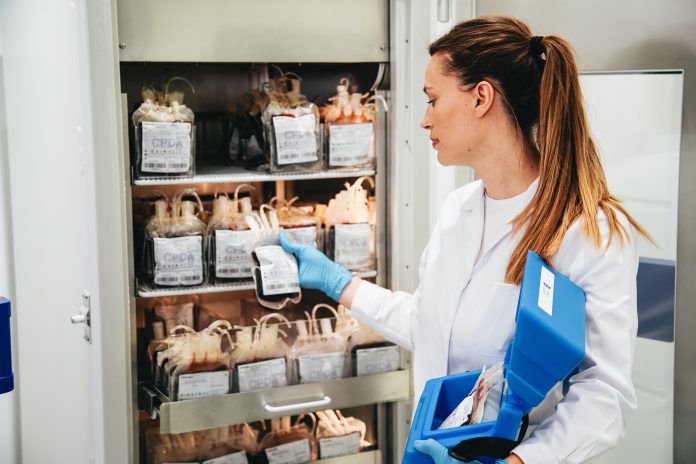
It is for this reason that for individuals affected by blood disorders such as haemophilia, the safety of blood products is vital. The Blood Management Solutions portfolio offered by B Medical Systems provides a complete range of products to store blood and its components.
Ensuring safe blood storage with B Medical Systems’ Blood Management Solutions
The company’s Blood Bank Refrigerators ensure blood samples are stored at the required temperature range of 2°C to 6°C. Specially designed for blood transfusion services, blood processing centres, blood banks, and hospitals, these medical cold chain solutions meet the highest regulatory requirements and deliver high performance in temperature control and energy consumption while offering remote monitoring capabilities.
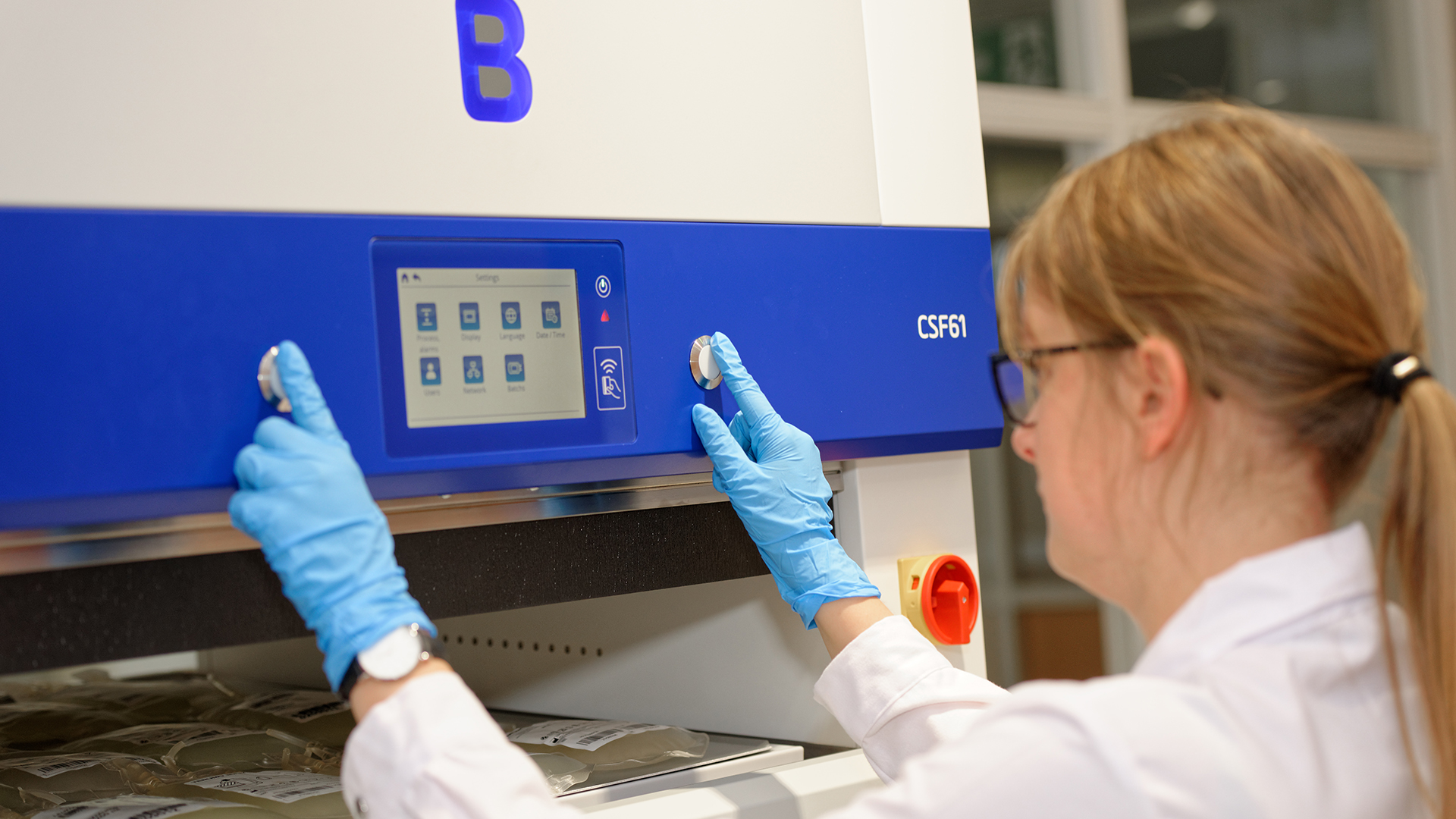
Blood samples are also used to obtain blood plasma which must be frozen rapidly and effectively to a core temperature of -30°C to ensure a high yield of proteins such as clotting factors.
This can be achieved using B Medical Systems’ Contact Shock Freezers, which provide one of the shortest freezing times available on the market. Their features ensure that plasma bags are homogeneously cooled and ready to be stored in a Plasma Storage Freezer or even an Ultra-Low Freezer capable of reaching the required storage temperature of below -30°C.
By using safe and reliable medical cold chain solutions when handling blood samples and blood components, the integrity of the clotting factors is maintained, and their recovery is also improved.
Fresh frozen human plasma is an important transfusion component and functions as a raw material to produce coagulation factor concentrates. It is, therefore, crucial that they are extracted and stored under strictly regulated and monitored conditions.